- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
18/5/2024
What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and can lead to both acute and chronic disease. Here's a detailed overview:
Causes and Transmission
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with infectious body fluids, such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions. Common ways it can be transmitted include:
- Mother to Child: During childbirth, an infected mother can pass the virus to her newborn.
- Sexual Contact: Unprotected sex with an infected partner.
- Needle Sharing: Sharing needles or other drug-injection equipment.
- Accidental Needle Sticks: Healthcare workers can be at risk due to needlestick injuries.
- Blood Transfusions: In areas where blood is not screened for HBV, transfusions can be a source of infection.
Symptoms https://www.highcpmgate.com/yhbakv50?key=f0db5a9bf4c2472da2c036528ce7be94https://www.highcpmgate.com/yhbakv50?key=f0db5a9bf4c2472da2c036528ce7be94https://www.highcpmgate.com/yhbakv50?key=f0db5a9bf4c2472da2c036528ce7be94
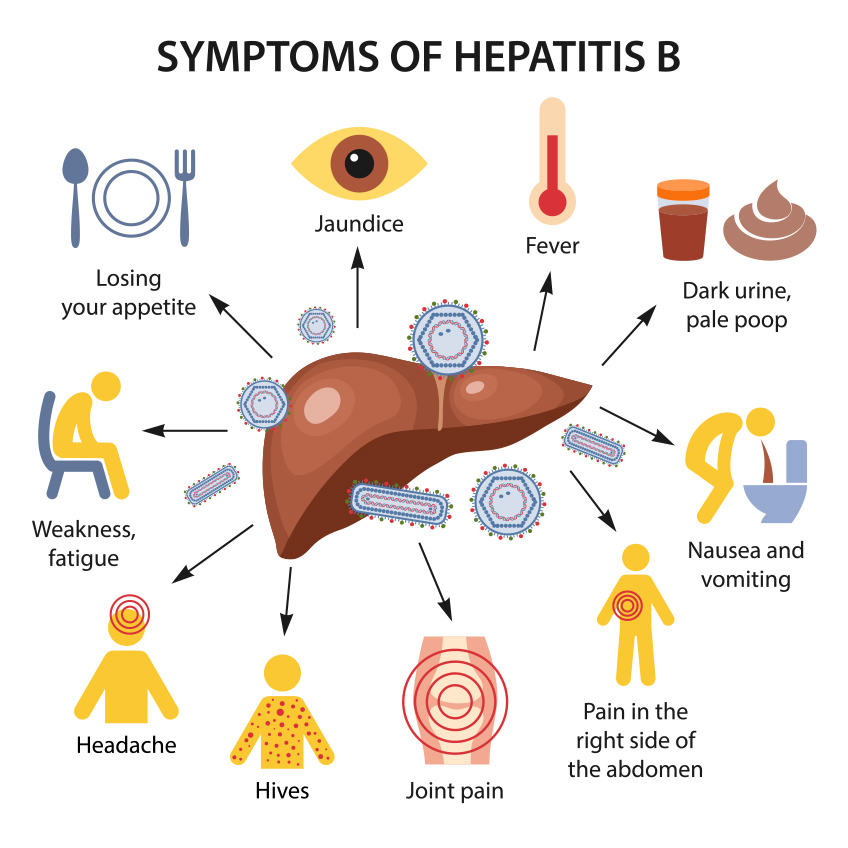
Symptoms of hepatitis B can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Acute Infection: Symptoms can appear 1 to 4 months after exposure and might include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-colored stool, joint pain, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
- Chronic Infection: Some people can develop a long-term infection that might be asymptomatic for years. Chronic hepatitis B increases the risk of developing severe liver diseases such as cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), liver failure, and liver cancer.
Diagnosis
Hepatitis B is diagnosed through blood tests that detect:
- HBsAg (Hepatitis B Surface Antigen): Indicates current infection.
- Anti-HBs (Antibody to Hepatitis B Surface Antigen): Indicates immunity either from past infection or vaccination.
- HBV DNA: Measures the amount of virus in the blood to assess the severity of the infection.
Treatment
Treatment for hepatitis B depends on whether the infection is acute or chronic:
- Acute Hepatitis B: Most people do not require treatment, as the infection often clears on its own. Supportive care to manage symptoms is usually provided.
- Chronic Hepatitis B: Antiviral medications can help reduce the virus's activity and prevent liver damage. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential to manage the condition and prevent complications.
Prevention
Prevention of hepatitis B involves:
- Vaccination: The hepatitis B vaccine is highly effective and is recommended for all infants, unvaccinated children and adolescents, and adults at risk.
- Safe Practices: Avoid sharing needles, use barrier protection during sex, and ensure blood products are screened for HBV.
- Mother-to-Child Transmission Prevention: Pregnant women should be screened for HBV, and if positive, appropriate measures should be taken to prevent transmission to the newborn, including vaccination and possibly antiviral treatment.
Prognosis
The prognosis for hepatitis B varies:
- Acute Hepatitis B: Most adults recover fully within six months.
- Chronic Hepatitis B: Long-term prognosis depends on the severity of liver damage and adherence to treatment. With proper management, individuals can lead healthy lives, but continuous monitoring is necessary to detect and manage any liver complications.
Overall, awareness, vaccination, and safe practices are key to preventing hepatitis B and managing its effects.
For Social media help Please click on this
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Nice information
ReplyDelete